In today's dynamic market and competitive environment, the ability to effectively manage finances is becoming a determining factor in business success. The Profit and Loss (PnL) report provides entrepreneurs and managers with the insights they need to make informed decisions aimed at improving the company's financial stability.
In the following sections of the article, we will take a detailed look at how the profit and loss statement is constructed, what key points should be taken into account when compiling it, and what benefits a business can receive through competent analysis and use of this financial instrument.
Example PnL report:
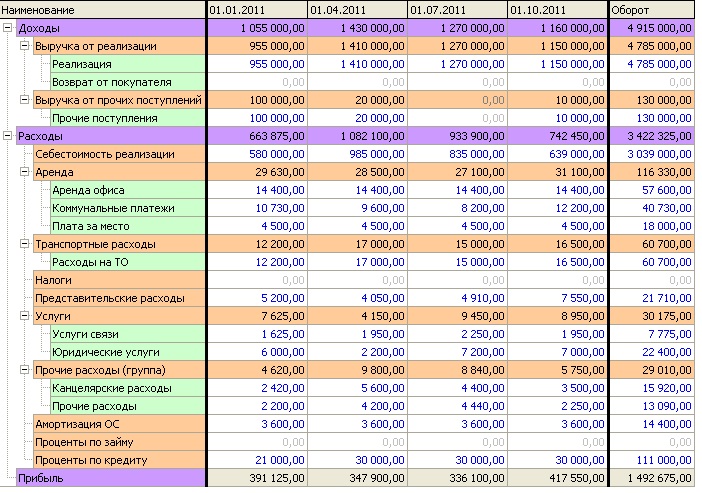
What is PnL
PnL (прибыли и убытки, PnL – это показатель, который выражает разницу между доходами и расходами бизнеса за определенный временной период. Слово «PnL» часто произносится как «пиэнель» и является ключевой метрикой для анализа финансового состояния компании, представленной в форме отчета о прибылях и убытках (PnL statement).
Features of the PnL report:
The PnL report covers the company's revenue for a selected period (e.g. month, quarter, year) and all associated expenses. It is important to note that both revenue and expenses, even expected ones, are recorded at the time of the transaction, using the accrual method. For example, when payment for goods is deferred, the revenue from the sale is reflected in the PnL report at the time of delivery of the goods, and the expenses are recorded when the goods are received, not at the time of payment.
Accounts receivable and accounts payable in PnL:
Accounts receivable:
Accounts receivable represent the amount of money a company is entitled to receive from its customers for goods or services rendered. Including accounts receivable in the PnL report allows you to see not only actual receipts, but also future expected revenues that have not yet been reflected in the company's accounts.
Example: If a company provides customers with deferred payment options, accounts receivable allow this expected income to be reflected in the PnL statement, creating a more complete financial picture.
Accounts payable:
Accounts payable, on the other hand, reflects the amounts a company is required to pay its suppliers for goods or services received. Including this element in PnL reflects the company's current obligations and provides information about what expenses will be recognized in future periods.
Example: If a company enters into an agreement with a supplier to pay in a few months, accounts payable allows this future expense to be reflected in the PnL report, providing a more detailed understanding of the current financial situation.
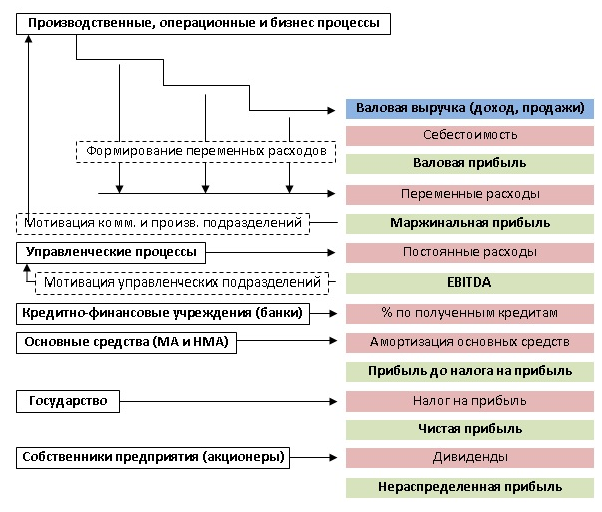
So, including accounts receivable and accounts payable in the PnL report not only reflects current cash flows, but also provides a more transparent view of the company's financial stability in the long term. This approach to financial analysis becomes an important tool for effective management and informed strategic decision-making.
Why do you need a PnL report:
- Financial status control:
- Determining the company's income and expenses for a selected period.
- Analysis of the success of sales of specific goods or services.
- Identifying profitable and unprofitable business processes.
- Identification of key costs such as packaging, shipping, rent, advertising.
- Assessing EBITDA and EBIT to determine a company's ability to service its debt.
- Determination of net profit, which reflects the real profit of the company.
- Performance Analysis for Investors:
- Investors can evaluate the performance of a business by taking into account revenues, expenses, and the bottom line.
- Investors can evaluate the performance of a business by taking into account revenues, expenses, and the bottom line.
- Making informed decisions:
- Helps businesses control their finances during payment delays and provides a clear picture of available funds.
- Allows you to avoid problems with cash flow gaps and make informed decisions about financial investments.

The PnL report not only provides an accurate picture of the company's financial position, but is also an essential tool for effective business management, informed decision-making and attracting investment.
How to Create a PnL Report: 9 Steps to Successful Financial Analysis
The PnL (profit and loss) report plays a key role in assessing the financial condition of a company for a certain period. Visually, it is a table that shows in detail all income and expenses for a month, quarter or year, and also calculates EBITDA, EBIT and net profit.
В крупных компаниях этот процесс часто автоматизирован, используя специализированные программы вроде «1С:Бухгалтерия» или аналогичные. Однако, в небольших компаниях формирование отчета PnL может проводиться вручную с использованием электронных таблиц, таких как Excel или «Google Таблицы».
Let's look at the 9 steps to creating a PnL report
- Income Identification:
- Specify all income for the selected period, for example, a month.
- Cost breakdown:
- Categorize all expenses, including materials, shipping, utilities, advertising, and taxes.
- Accounting for material costs:
- Determine the cost of materials for production
- Delivery and utilities:
- Separate shipping and utility costs
- Advertising expenses:
- Take into account advertising costs
- Payment of taxes:
- Determine the amount of taxes paid
- Calculation of EBITDA and EBIT:
- Calculate EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization) and EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes).
- Net profit:
- Determine net profit by reflecting the actual financial results of the business for the period.
- Analysis of changes:
- Assess the dynamics of changes in indicators and make decisions based on the data obtained.
By following these steps, you can effectively create a PnL report for your business and get a complete picture of its financial position.
Step 1. Recording revenue: Revenue represents the total income a company receives from its activities, including sales of goods, performance of work, and provision of services. Such information is conveniently tracked through online cash registers or financial accounting programs, which are widely used in business.
Step 2. Recording Variable Costs: These costs include expenses that vary with production and sales volumes, such as the purchase of raw materials, supplies, and the cost of delivering goods to customers.
In this case, variable costs include the cost of materials and delivery of finished bags and backpacks.
Step 3. Gross Profit Calculation: This figure shows how much money is left after variable expenses are subtracted from revenue.
To calculate gross profit, you need to subtract variable expenses from revenue.
Step 4. Recording fixed expenses: These expenses are always present, even if the business does not generate revenue. Examples include rent, utilities, and salaries of full-time employees.
In this case, fixed costs are utility costs and advertising.
Step 5. Calculation of EBITDA: This is a measure of a company's profit before interest on loans, taxes, and depreciation. In other words, it is operating profit.
To calculate EBITDA, you subtract fixed costs from gross profit.
Step 6. Recording of depreciation: Depreciation is a gradual reduction in the value of fixed assets and intangible assets in accordance with their wear and tear, including this process in the cost of the company's products and services.
To illustrate, to calculate the depreciation costs of, for example, a vehicle, you need to divide its cost by its service life. If the cost of the car is 900,000 rubles, and the service life is 5 years, then the monthly depreciation amount will be 900,000 rubles / 5 years / 12 months = 15,000 rubles.
Step 7. Calculating EBIT: This is the profit before interest on loans and tax expenses. To determine it, depreciation should be subtracted from operating profit (EBITDA).
Step 8. Registration of expenses for taxes and interest on loans: The amount of taxes depends on the conditions of the tax system in which the business operates. In this example, the self-employed person's tax for the month was 4,000 rubles.
Interest on loans is the amount of interest in monetary terms for the PnL reporting period. Let's assume that a self-employed person took out a loan of 100,000 rubles for a year at 10% per annum. His payment schedule will look like this: the PnL report must include the value for May from the "Interest repayment" column - 833.33 rubles.
Step 9. Calculating net profit: This is the profit after deducting all expenses, interest on loans, income tax, and depreciation. This figure shows how much money the business has brought in over a certain period. In the example provided, the self-employed person's net profit was 23,928.67 rubles.
PnL Report Highlights: Unique Perspective and Key Points
Отчёт PnL (Profit and Loss), буквально означающий «доходы и расходы», играет важную роль в анализе финансового состояния компании. Этот документ, создаваемый методом начисления, не просто отражает статистику доходов и расходов за определённый период. Его сущность состоит в фиксации данных в момент совершения операции, что предоставляет более точное представление о реальном финансовом положении предприятия.
A PnL report is more than just a set of numbers; it is a powerful tool for monitoring finances and making informed business decisions. Tracking income and expenses in real time allows business leaders to respond to changes in the economic environment.
Conclusion:
As a result, the profit and loss statement (PnL) becomes an indispensable tool for those who strive to successfully manage a business. Careful and competent preparation of the PnL allows entrepreneurs and financial managers to penetrate into the depth of the company's financial activities, revealing not only numbers, but also strategic opportunities.
Assessing revenue and expenses, analyzing variable and fixed costs, and accounting for accounts receivable and payable provide a complete and accurate financial picture. These tools help you identify successful trends, manage costs, and make informed business decisions.
Drawing up a PnL is not just an accounting formality, but the key to effective management, achieving financial stability and forming a business development strategy. Knowing how to use this tool correctly opens the door to a successful and sustainable future in the business world. Let the PnL become your reliable guide in realizing your entrepreneurial ambitions, helping you reach new heights and confidently meet all the challenges of the business world.








