An idea is the foundation of business. Every business began with an idea and evolved into something greater: whether it was the creation of a product, a company, or a startup.
Today, startups are popular due to their innovative ideas. Startup founders are turning their hobbies into their life's work. Is it talent? Not only that. Above all, it's hard work, self-improvement, and self-organization. So what makes a startup so appealing? Find out in this article.
What is a startup and how is it different from an established business?
A startup is a project idea in need of funding. Startups are not established projects known to the world. Instead, they are unique, unusual commercial ideas.
Unlike an established business, a startup isn't a ready-made business model with every step worked out. Business plans for such projects don't often work out. However, they can, after some time, if an investor is found.
Here are some of the characteristics of a startup project:
- The uniqueness of the project, project ideas and implementation methods;
- Attracting investment is a necessity;
- Short launch times.
How to choose the right direction
Not every new business venture takes off successfully. It's important to understand that a well-thought-out plan doesn't guarantee a project's success. An idea or desire alone isn't enough. Of course, a strong desire and an interesting idea are a huge plus. However, it's more about talent, hard work, interest, and an understanding of what you'll be paid for.
To begin with, it’s worth asking yourself some banal questions:
- What will I do?
- What activities will I carry out?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What market am I going to enter?
- How and what product will solve the problems for the selected audience?
- Financial part: how much money is required for your business model?
When asking questions like these, answer honestly. Take notes and detail. They'll help you get closer to the ideal.

What is the essence of a startup?
The essence of a startup is that over time, the business model becomes viable over the long term.
At first, a startup doesn't fully pay for itself. A working model may initially reach break-even. After some time, it will begin to generate income, expand, and become a major business.
Startups attract investors. Without an investor, it's difficult to take the first steps. An innovative idea, attracting investors, and a short implementation time are the main differences between a startup and a business.
How to choose a target audience and market for a project?
It's important to understand clients' problems and then offer solutions. How do you do this? The answer is obvious: conduct a focus group survey. To do this, choose a location (a café, coworking space, or other public space) or a method of communication (message, social media, or email surveys). Prepare survey questions in advance. It's best to leave them open-ended to encourage detailed responses. Important: don't involve relatives—the likelihood of biased responses may increase, leading to inaccurate results.
Some easy questions to start with:
- What is your main problem?
- What helps with its solution?
- What other solutions to the problem can you think of?
Expand the list of questions. Surveys are conducted before the launch. Identifying needs will allow you to more quickly identify pain points and find a solution for the client's problem. This creates a goal for the startup.
Why is this important? Launching or creating a product requires research. Research helps determine whether a problem is solvable, how it can be solved, and what solutions can be proposed.
Before launching, the market size is also determined. To determine the market size, an analysis of competitors in the chosen industry or segment is conducted: how many there are, what prices, services, and products they offer. This analysis will help you understand how unique and viable your product is. It's worth noting that viability is a key factor in both the success and future development of a commercial project.
Calculating market size doesn't necessarily require precise figures (approximate figures are also suitable). The volume of users (customers) is also considered. For example, you plan to open an online store selling unique handmade silver jewelry in a given region. The primary audience is women aged 18 to 40. Let's say there are approximately 200,000 girls and women of this age group living in the chosen region. That's two hundred thousand potential customers. Of this number, 501,000,000 are likely to be active, or perhaps 251,000,000. At this stage, many factors are taken into account: those who don't know how to use the internet, those who prefer shopping, and so on. The remaining number is the number willing to cooperate. Understanding the approximate number of customers allows you to calculate the estimated profit. Therefore, creating surveys helps not only identify areas for development but also describe your future client, their needs, and the potential profit.
Target audience analysis
The first step is to create a consumer profile: age, region, interests, hobbies, passions, average income, places they frequent, needs—everything that characterizes the target group. A consumer profile allows for a better understanding of the potential client, pricing, product format and style, and, most importantly, how to position the product in the market.
Market analysis: competitors, SWOT analysis
Market analysis is conducted to study competitors. We previously wrote about market size. This factor is taken into account to understand market share.
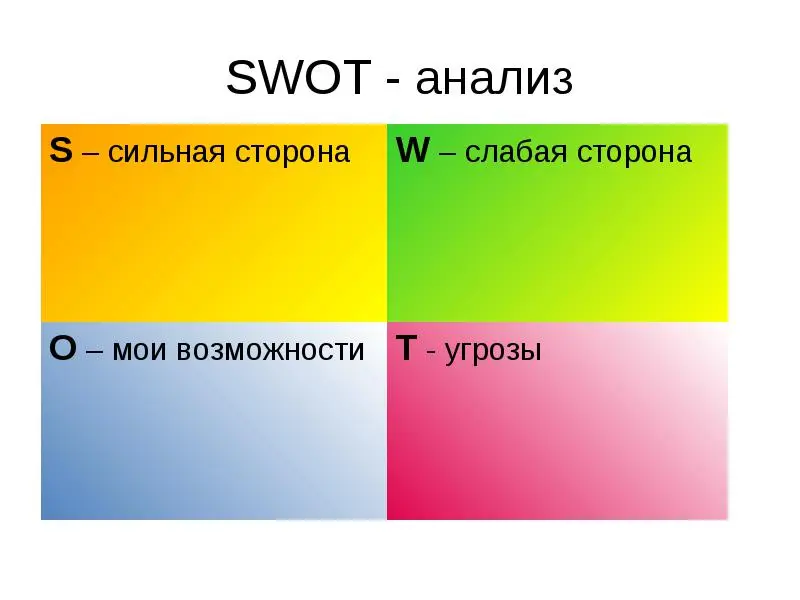
The market may be saturated with competitors offering no innovation. Perhaps there are no competitors, allowing you to become a pioneer and carve out your niche. However, to better understand the strengths and weaknesses of both your company and your competitors, can be carried out SWOT analysis.
A SWOT analysis is an examination of an organization's strengths and weaknesses. It doesn't matter who owns the company. This method is a comprehensive approach. The following factors are taken into account:
- Strengths (S) – these include key advantages, such as market share, increased sales through various events, good service (fast delivery, customer service, friendly communication), and business hours;
- Weaknesses (W) – weaknesses in an organization, such as poor service, missed delivery dates, or weak marketing – are what hinder growth;
- Opportunities (P) – opportunities for development. For example, staff training, implementing marketing offers beyond the usual scope, new suppliers or logistics partners – these are what allow an organization to expand, develop, and grow;
- Treats (T) – threats related to external factors beyond your control. These threats include natural disasters, legislative changes, and other similar situations.
A SWOT analysis expands the boundaries of what's visible. Until you begin analyzing, you won't notice any shortcomings or flaws. After analysis, your understanding of the direction you're moving toward becomes clearer. A clear picture emerges: what to do, how to act, and how to behave in the marketplace.
Team
People are, of course, a company's most important resource. Without people, there are no ideas and no progress. The team builds the company's future. It's important to gather like-minded people, develop them, and develop ourselves to move forward. Many startups started small, united by a common goal. A successful start-up is a small part of the process. It's important to stay afloat over the long term. Then the organization will begin to expand, and the team will be replenished with new people.
Don't forget about the working conditions. Every employee needs a comfortable place where they can be listened to, supported, and motivated (including financially). Employees are like family.
MVP. How to define a minimum set of features?
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is a product with a minimal set of features to meet customer needs. It's a kind of large-scale test version. An MVP is refined over time based on customer needs. The minimum solution is ready, and we can move forward. If a minimum solution doesn't yet exist, then we need to define a minimum set of features.
When we talk about a minimal set of features, we're not talking about minimalism. Simplicity should be useful and satisfy the customer's needs. To achieve this, you can adhere to:
- Hypothesis testing. A hypothesis is the initial step. It requires testing and then analyzing the results. There can be multiple hypotheses. Identify a few key ones. Test them with a focus group, asking direct, open-ended questions. For example, what they would improve in your product, what problem your product can solve, and so on.
- Potential buyers. Identify potential customers from a large number of people surveyed. These are people interested in your product. Enter their information into a database so you can contact them later and make an offer;
- Visual. Visual perception has a significant impact. It's important to create a beautiful visual form to be memorable;
- Testing. Offer a compelling offer to users to evaluate the product. They will add the desired features to the client;
- Refinements and demand. Demand creates supply; price is determined. After refining the product, test demand and price. Find the sweet spot for which consumers are willing to pay a certain amount.
Forecasting
The forecasting stage is complex and labor-intensive. At this stage, the business's growth potential and scalability are assessed. If a business doesn't scale, it will likely quickly founder. Forecasting allows for the consideration of various scenarios.
Profit forecasting is the first thing that requires calculation. A company's economics are calculated by taking into account costs and identifying profits that allow for growth.
Profit forecasting is the basis of a startup business plan.

Conclusion
Launching a startup is no easy task. The market is saturated with an abundance of services and products. However, the world does not stand still. Development leads to innovative ideas for solving problems. Therefore, it is essential to carefully develop and think through a startup plan. There must be a viable business model designed for the long term. At the same time, the business model must be attractive to investors so that they will invest in it.







